|
I am a fourth year PhD candidate at The University of Texas Austin, advised by Prof. Constantine Caramanis and Prof. Sanjay Shakkottai. My research focuses on the theoretical foundations of generative models (e.g. diffusion, flows and optimal transport) and their applications in conditional sampling (e.g. inverse problems, language modeling, personalization, planning, and reasoning). I am currently working as a student researcher at Google. Prior to UT Austin, I worked as a Scientist/Engineer-SD at ISRO. I received my BTech from IIST. I was fortunate to be advised by Prof. Rama Krishna Gorthi and Prof. Deepak Mishra during my undergraduate research. |

|
|
|
|
|
|
Discrete Diffusion

|
NEW
Litu Rout, Andreas Lugmayr, Yasamin Jafarian, Srivatsan Varadharajan, Constantine Caramanis, Sanjay Shakkottai, and Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman ArXiv, 2025 Project Page PDF ArXiv Code We introduce Anchored Posterior Sampling (APS) for masked diffusion foundation models, built on two key innovations: (i) quantized expectation, which provides gradient-like guidance for discrete diffusion with purely discrete embedding space, and (ii) anchored remasking, which enables adaptive decoding during inference. Our method supports a variety of linear and nonlinear image restoration tasks, as well as mask-based garment styling and reference-guided style transfer. |

|
NEW
Litu Rout, Constantine Caramanis, and Sanjay Shakkottai NeurIPS, 2025 Project Page PDF ArXiv Code 
Diffusion Language Models (DLMs) promise parallel generation and bidirectional context, yet they underperform autoregressive (AR) models in both likelihood modeling and generated text quality. We address this issue by introducing Anchored Diffusion Language Model (ADLM), a novel two-stage framework that first predicts distributions over important tokens via an anchor network, and then predicts the likelihoods of missing tokens conditioned on the anchored predictions. |
Continuous Diffusion & Rectified Flows
|
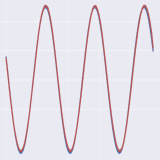
Sai Shankar Narasimhan, Shubhankar Agarwal, Litu Rout, Sanjay Shakkottai, Sandeep Chinchali NeurIPS, 2025 PDF ArXiv We present Constrained Posterior Sampling (CPS), a scalable diffusion sampling process that generates realistic time series samples that belong to a constraint set. Without any additional training, CPS can handle a large number of constraints without sacrificing sample quality. We provide a detailed theoretical analysis of the effect of modifying the traditional diffusion sampling process with CPS. |

|
ICLR
Litu Rout, Yujia Chen, Nataniel Ruiz, Constantine Caramanis, Sanjay Shakkottai, and Wen-Sheng Chu ICLR, 2025 OpenReview Project Page PDF Code  ComfyUI
ComfyUI
 Tweet
Tweet
We present an efficient inversion method for RF models, including Flux, that requires no additional training, latent optimization, prompt tuning, or complex attention processors. We develop a new vector field for RF inversion, interpolating between two competing objectives: consistency with a possibly corrupted input image, and consistency with the “true” distribution of clean images. |

|
ICLR (Oral)
Litu Rout, Yujia Chen, Nataniel Ruiz, Abhishek Kumar, Constantine Caramanis, Sanjay Shakkottai, and Wen-Sheng Chu ICLR, 2025 OpenReview Project Page PDF ArXiv Code  Demo
Tweet
Demo
Tweet
We introduce Reference-Based Modulation (RB-Modulation), a training-free plug-and-play solution for content and style personalization. By incorporating style features into the controller’s terminal cost, we modulate the drift field in diffusion models’ reverse dynamics, enabling training-free personalization. Further, we propose an Attention Feature Aggregation (AFA) module that decouples content from the reference style image. |

|
Negin Raoof, Litu Rout, Giannis Daras, Sujay Sanghavi, Constantine Caramanis, Sanjay Shakkottai, and Alex Dimakis ICLR, 2025 We introduce Infilling Score, a new method for pre-training data detection in Large Language Models based on token-level infilling likelihoods. Infilling Score can be computed for autoregressive models without re-training using Bayes rule. A naive application of Bayes rule scales linearly with the vocabulary size. However, we propose a ratio test-statistic whose computation is invariant to vocabulary size. |
|
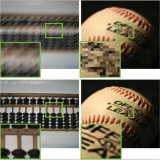
Litu Rout, Yujia Chen, Abhishek Kumar, Constantine Caramanis, Sanjay Shakkottai, and Wen-Sheng Chu CVPR, 2024 Project Page PDF ArXiv Code 
We present an efficient second-order approximation using Tweedie's formula to mitigate the bias incurred in the widely used first-order samplers. With this method, we devise a surrogate loss function to refine the reverse process at every diffusion step to address inverse problems and perform high-fidelity text-guided image editing. |

|
NeurIPS
Litu Rout, Negin Raoof, Giannis Daras, Constantine Caramanis, Alex Dimakis, and Sanjay Shakkottai NeurIPS, 2023 OpenReview Poster ArXiv Code  Demo
Presentation
Tweet
Demo
Presentation
Tweet
Solving inverse problems (e.g. inpainting/deblurring) for general domain images is hard. Magic Eraser and other commercial tools use separately trained models for each task. We introduce PSLD, a method that uses Stable Diffusion to solve all linear problems without any extra training. |
|
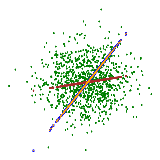
Litu Rout, Advait Parulekar, Constantine Caramanis, and Sanjay Shakkottai UT Austin Technical Report, 2023 ArXiv We provide a theoretical justification for sample recovery using diffusion based image inpainting in a linear model setting. Unlike most inpainting algorithms, we prove that diffusion based inpainting generalizes well to unseen masks without retraining. Motivated by our analysis, we propose a modified RePaint algorithm we call RePaint+ that provably recovers the underlying true sample and enjoys a linear rate of convergence. |

|
Matthew Faw*, Litu Rout*, Constantine Caramanis, and Sanjay Shakkottai COLT, 2023 (* Equal contribution) ArXiv We develop a technique that allows us to prove convergence rates for (L0, L1)-smooth functions without assuming uniform bounds on the noise support. The key innovation behind our results is a carefully constructed stopping time. This is simultaneously large on average and allows us to decorrelate the adaptive stepsizes from the gradients, which is a major challenge in many analyses. |
Optimal Transport

|
ICLR
Litu Rout, Alexander Korotin, and Evgeny Burnaev ICLR, 2022 OpenReview PDF ArXiv Slides Poster Code 
While Optimal Transport (OT) cost serves as the loss for popular generative models, we demonstrate that the OT map can be used as the generative model itself. Previous analogous approaches consider OT maps as generative models only in the latent spaces due to their poor performance in the original high-dimensional ambient space. In contrast, we fit OT maps directly in the ambient space, e.g., a space of high-dimensional images. |

|
Khai Nguyen, Tongzheng Ren, Huy Nguyen, Litu Rout, Tan Nguyen, and Nhat Ho ICLR, 2023 OpenReview PDF ArXiv A major concern of Sliced Wasserstein (SW) distance is that it requires a large number of projections in high-dimensional settings. To address this concern, we derive projections from a small number of bottleneck projections. We introduce Hierachical Radon Transform (HRT) that recursively applies Radon Transform (RT). We design Hierarchical Sliced Wasserstein (HSW) distance to estimate the discrepancy between measures in high dimensions. |

|
Milena Gazdieva*, Litu Rout*, Alexander Korotin*, Alexander Filippov, and Evgeny Burnaev Preprint, 2022 (* Equal contribution) ArXiv First, we prove that GANs with content or identity losses learn optimal transport (OT) maps between source and target measures in super-resolution tasks. Second, we empirically demonstrate that these learned OT maps are biased and provide an OT solver to recover an unbiased OT map. It provides nearly state-of-the-art performance on the unpaired AIM19 benchmark without having to use content or identity losses. |
Generative Adversarial Networks

|
AAAI
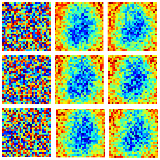
Litu Rout AAAI (21% acceptance), 2021 PDF ArXiv Slides Poster Teaser Presentation In this paper, we intend to demystify an interesting phenomenon: adversarial interaction in GANs creates non-homogeneous equilibrium by inducing Turing instability in a Pseudo-Reaction-Diffusion (PRD) model. This is in contrast to supervised learning where the identical model achieves homogeneous equilibrium. |
|
Litu Rout NeurIPS ML4PS Workshop, 2020 PDF ArXiv In this study, we observe that a system in which a generator and a discriminator adversarially interact with each other exhibits Turing-like patterns in the hidden layer and top layer of the generator. |

|
Litu Rout CVPR Adversarial ML Workshop, 2021 Despite numerous attempts sought to provide empirical evidence of adversarial regularization outperforming sole supervision, the theoretical understanding of such phenomena remains elusive. In this study, we aim to resolve whether adversarial regularization indeed performs better than sole supervision at a fundamental level. |
|
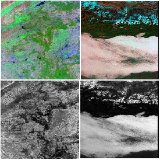
Litu Rout TGRS (impact factor: 5.85), 2020 PDF Preprint In this article, we devise a method, which we call ALERT, to tackle missing band reconstruction. The proposed method reconstructs missing band with the sole supervision of spectral and spatial priors. |
|
Litu Rout, Indranil Misra, S Manthira Moorthi, and Debajyoti Dhar CVPR Earth Vision Workshop, Oral Talk, 2020 PDF ArXiv This paper seeks to address synthesis of high resolution multi-spectral satellite imagery using adversarial learning. Guided by the discovery of attention mechanism, we regulate the process of band synthesis through spatio-spectral Laplacian attention. |
Satellite Image Processing

|
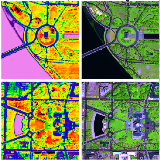
Litu Rout, Saumyaa Shah, S Manthira Moorthi, and Debajyoti Dhar CVPR Earth Vision Workshop, Oral Talk, 2020 PDF ArXiv In this study, we propose to parameterize action variables by matrices, and train our policy network using Monte-Carlo sampling. We study the implications of parametric action space in a model-free environment from theoretical and empirical perspective. |
|
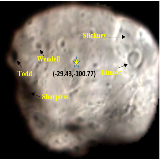
Indranil Misra, Litu Rout, Sunita Arya, Yatharath Bhateja, S Manthira Moorthi, and Debajyoti Dhar Planetary and Space Science , 2021 PDF Preprint This paper describes the techniques developed to enhance the Phobos image from MCC multi-frame acquisitions using image rectification and topographic data. After incorporating these techniques, the final Phobos image appears more representative, spatially enhanced, and has normalized radiometry to study its surface features. |
Visual Object Tracking
|
Matej Kristan, Ales Leonardis, Jiri Matas, Michael Felsberg, Roman, Pflugfelder, Litu Rout and others ECCV VOT Workshop, 2022 Results of over ninety trackers are presented; many are state-of-the-art trackers published at major computer vision conferences or in journals in the recent years. |

|
Matej Kristan, Ales Leonardis, Jiri Matas, Michael Felsberg, Roman, Pflugfelder, Litu Rout and others ICCV VOT Workshop, 2019 Results of 81 trackers are presented; many are state-of-the-art trackers published at major computer vision conferences or in journals in the recent years. |
|
Litu Rout, Priya Mariam Raju, Deepak Mishra, and Rama Krishna Gorthi ACCV, 2018 PDF ArXiv Here, we propose a robust framework that offers the provision to incorporate illumination and rotation invariance in the standard Discriminative Correlation Filter (DCF) formulation. We also supervise the detection stage of DCF trackers by eliminating false positives in the convolution response map. |
|
|
Litu Rout, Deepak Mishra and Rama Krishna Gorthi ECCV VOT Workshop, 2018 This paper discusses a novel approach to regress in temporal domain, based on weighted aggregation of distinctive visual features and feature prioritization with entropy estimation in a recursive fashion. |
|
|
Litu Rout, Sidhartha, Deepak Mishra, and Rama Krishna Gorthi WACV, 2018 PDF ArXiv Code In this paper, we study the necessity to capture various physical constraints through motion consistency which has been demonstrated to improve accuracy, robustness and more importantly rotation adaptiveness. |
|
|
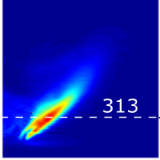
Litu Rout, Rajesh Sadanandan and Deepak Mishra Sadhana, Indian Academy of Sciences, 2019 The developed algorithm has been implemented to yield the physically significant chemiluminescence emission from hydroxyl radicals in flames from line-of-sight integrated images. The effectiveness of this algorithm is highlighted using exemplary OH chemiluminescence images captured from a standard swirl stabilized research burner. |
Patent
|
Tapan Misra, Litu Rout SAC, ISRO, 2020 Patent No. 346206, Application No. 202041004166 The present embodiment proposes an efficient Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) based hyper-spectral image compression technique to store multiple acquisitions over same region of interest and thereby, improve Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) of hyper-spectral images which usually have coarse spatial resolution. |
Chapters

|
Litu Rout, Priya Mariam Raju, Deepak Mishra, and Rama Krishna Gorthi Computer Vision – ACCV, 2018 In this chapter, we propose a robust framework that offers the provision to incorporate illumination and rotation invariance in the standard Discriminative Correlation Filter (DCF) formulation. We also supervise the detection stage of DCF trackers by eliminating false positives in the convolution response map. |

|
Litu Rout, Deepak Mishra and Rama Krishna Gorthi Computer Vision – ECCV Workshops, 2018 This chapter discusses a novel approach to regress in the temporal domain, based on weighted aggregation of distinctive visual features and feature prioritization with entropy estimation in a recursive fashion. |
Reviewer & Program Committee Member
|